griddb.github.io
— Overview —
Purpose of this document
This document explains how to use the GridDB Dockerfile sample.
Precautions
Make sure you can connect to the Internet. If you are behind a proxy, uncomment the proxy settings in the Dockerfiles.
— GridDB Dockerfile sample —
Overview
You can use GridDB Dockerfile sample to create GridDB server image and GridDB client image. You can run GridDB server and GridDB client on docker hosts.
Architecture
GridDB Dockerfile sample includes two types of Dockerfile:
-
Dockerfile for GridDB server
Used to build GridDB server image
-
Dockerfile for GridDB client
Used to build GridDB client image which can run operation tools, SQL interface, Java library, and WebAPI
After building GridDB server and client image successfully, you can run these images to compose a GridDB cluster or you can push them in a container registry then you are able to pull them from other machines.
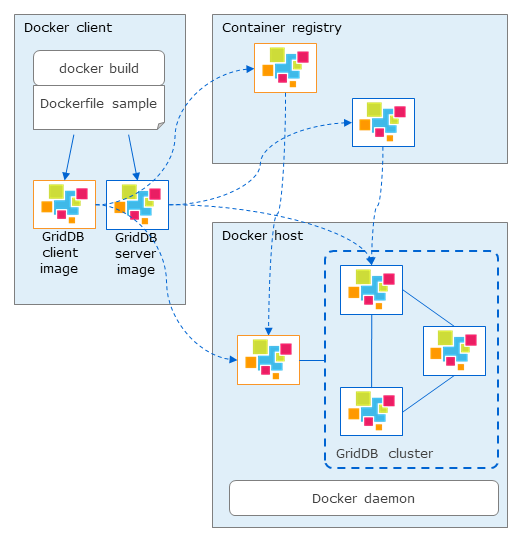
Component of GridDB Dockerfile sample
- Docker_server/: GridDB server directory
- rpm/: GridDB installer directory
- Dockerfile_server
- docker-entrypoint_server.sh
- Docker_client/: GridDB client directory
- 3rd/: external software directory
- rpm/: GridDB installer directory
- Dockerfile_client
- docker-entrypoint_client.sh
- Provider/:
- Provider
- provider.json
- sample/:
- JDBCClient.java
- MultiNodesClient.java
- docker-compose.yml: config file for docker-compose
- .env: environment variables for docker-compose
Supported environment condition
GridDB Dockerfile sample has been confirmed to work in the following
-
On-premises:
- Host OS: RHEL / CentOS 8.3
- Docker: Docker CE 20.10.10 (with docker-compose V1.21.2)
This sample has been tested and proven compatible with GridDB Enterprise Edition 5.0.
— How to use GridDB Dockerfile sample on-premise —
Build image
Build GridDB server image
Copy the following files to Docker_server\rpm directory:
$ ls rpm
griddb-ee-client-5.0.0-linux.x86_64.rpm
griddb-ee-server-5.0.0-linux.x86_64.rpm
Execute the following command in the Docker_server directory to build GridDB server image:
$ docker build -t griddb/griddb-server:5.0 -f Dockerfile_server .
Build GridDB client image
Copy the following files to Docker_client\rpm directory:
$ ls rpm
griddb-ee-client-5.0.0-linux.x86_64.rpm
griddb-ee-java-lib-5.0.0-linux.x86_64.rpm
griddb-ee-webapi-5.0.0-linux.x86_64.rpm
griddb-ee-webui-5.0.0-linux.x86_64.rpm
Copy the following file to Docker_client\3rd directory:
- Java SE 8 (jdk-8uXXX-linux-x64.rpm)
Execute the following command in the Docker_client directory to build GridDB client image:
$ docker build -t griddb/griddb-client:5.0 -f Dockerfile_client .
Run GridDB image
Run GridDB server image
Use the following command to start GridDB server container built in the previous section:
$ docker run -d --name <docker_container_name> \
-e GRIDDB_CLUSTERNAME=<cluster_name> \
-e GRIDDB_NODE_NUM=<node_number> \
-e NOTIFICATION_ADDRESS=<notification_address> \
griddb/griddb-server:5.0
The following environment variables need to be specified when starting GridDB server container:
| Enviroment variable name | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
| GRIDDB_CLUSTERNAME | cluster name | myCluster |
| GRIDDB_NODE_NUM | number of nodes of the cluster | 1 |
| NOTIFICATION_ADDRESS | multicast address (MULTICAST mode) | (*1) |
| NOTIFICATION_MEMBER | list of IP addresses of nodes, separated by comma (FIXED_LIST mode) | (*1) |
| NOTIFICATION_PROVIDER | provider url (PROVIDER mode) | (*1) |
| SERVICE_ADDRESS | ip address of a node | - |
(*1) only specify one of them
Run GridDB client image
Use the following command to start GridDB client container built in the previous section:
$ docker run -d --name <docker_container_name> \
-e GRIDDB_NODE=<node_ip> \
-e GRIDDB_PORT=<node_operation_port> \
griddb/griddb-client:5.0
The following environment variables need to be specified when starting GridDB client container:
| Enviroment variable name | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
| GRIDDB_NODE | IP address of a node (any node) | -(required) |
| GRIDDB_PORT | port of a node | -(required) |
Compose a GridDB cluster (on the same Docker host)
Single node
-
Start GridDB cluster
Start a GridDB server container and build a cluster with a single node configuration.
Run the following command. The container name is griddb:
$ docker run -d --name griddb \ -e GRIDDB_CLUSTERNAME=<cluster_name> \ -e GRIDDB_NODE_NUM=1 \ -e NOTIFICATION_ADDRESS=<notification_address> \ griddb/griddb-server:5.0Use –mount option persisting data GridDB home directory as a docker volume:
$ docker run -d --name griddb \ -e GRIDDB_CLUSTERNAME=<cluster_name> \ -e GRIDDB_NODE_NUM=1 \ -e NOTIFICATION_ADDRESS=<notification_address> \ --mount source=<volume_name>,target=/var/lib/gridstore/ \ griddb/griddb-server:5.0 -
Connect from GridDB client
Connect with NoSQL API:
$ cd sample $ javac -cp /usr/share/java/gridstore.jar SingleNodeClient.java $ java -cp .:/usr/share/java/gridstore.jar SingleNodeClient <IP Address> 10001 myClusterConnect with JDBC:
$ cd sample $ javac JDBCClient.java $ java -cp .:/usr/share/java/gridstore-jdbc.jar JDBCClient <IP Address> 20001 myCluster -
Connect from GridDB client container
Specify a running GridDB server by –link option and start the GridDB client container.
$ docker run -d --name griddb-client \ --link <container_name>:griddb \ griddb/griddb-client:5.0
Multiple nodes
The following steps will start and compose a three-node GridDB cluster and GridDB home directory of each node is persisted. The client container will also run on the same docker host.
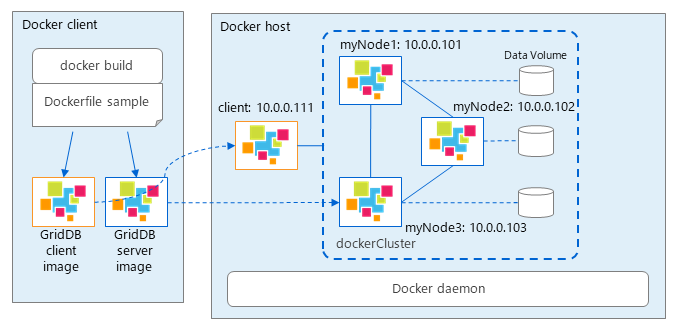
By using docker-compose.yml file, you can start multiple containers including client at once:
version: '3'
services:
griddb1:
container_name: myNode1
image: griddb-server:${GRIDDB_VERSION}
build:
context: ./Docker_server
dockerfile: Dockerfile_server
env_file: .env
networks:
griddb_net:
ipv4_address: ${IPADDR_NODE1}
volumes:
- "node1:/var/lib/gridstore/"
griddb2:
container_name: myNode2
image: griddb-server:${GRIDDB_VERSION}
env_file: .env
networks:
griddb_net:
ipv4_address: ${IPADDR_NODE2}
volumes:
- "node2:/var/lib/gridstore/"
griddb3:
container_name: myNode3
image: griddb-server:${GRIDDB_VERSION}
env_file: .env
networks:
griddb_net:
ipv4_address: ${IPADDR_NODE3}
volumes:
- "node3:/var/lib/gridstore/"
client:
container_name: client
image: griddb-client:${GRIDDB_VERSION}
build:
context: ./Docker_client
dockerfile: Dockerfile_client
env_file: .env
networks:
griddb_net:
ipv4_address: ${IPADDR_CLIENT}
volumes:
- "client:/var/lib/gridstore/log"
depends_on:
- "griddb1"
- "griddb2"
- "griddb3"
ports:
- 8080:8080
- 8081:8081
volumes:
node1:
node2:
node3:
client:
networks:
griddb_net:
driver: bridge
ipam:
config:
- subnet: ${SUBNET}
Define environment variable corresponding to the GridDB cluster connection method (FIXED_LIST, MULTICAST, PROVIDER).
The environment variables for starting container in section 3.2 and for above docker-compose are described in .env file:
| Environment variable | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| GRIDDB_NODE_NUM | number of nodes of the cluster | 3 |
| GRIDDB_CLUSTERNAME | cluster name | dockerCluster |
| GRIDDB_VERSION | version | 5.0 |
| NOTIFICATION_ADDRESS | multicast address (MULTICAST mode) | 239.0.0.1 |
| NOTIFICATION_MEMBER | list of IP addresses of nodes, separated by comma (FIXED_LIST mode) | 172.18.0.2,172.18.0.3,172.18.0.4 |
| NOTIFICATION_PROVIDER | provider url (PROVIDER mode) | http://providerhost/provider.json |
| GRIDDB_NODE | IP address of a node (any node) | 172.18.0.2 |
| GRIDDB_PORT | port of a node | 10040 |
| IPADDR_NODE1 | IP address of myNode1 | 172.18.0.2 |
| IPADDR_NODE2 | IP address of myNode2 | 172.18.0.3 |
| IPADDR_NODE3 | IP address of myNode3 | 172.18.0.4 |
| IPADDR_CLIENT | IP address of client | 172.18.0.5 |
| SUBNET | subnetwork of the cluster | 172.18.0.0/24 |
Compose a GridDB cluster (multiple Docker hosts)
Starting multiple containers on the same docker host in previous section does not provide the full benefit of clustering in the following respects:
- Ensure availability through node redundancy
- High-speed processing by parallel use of independent resources
Building a GridDB cluster on multiple docker hosts offers these benefits.
MULTICAST method
When building cluster in MULTICAST mode, the network of container must be host mode.
The following commands will build a three-node GridDB cluster on 3 docker hosts in MULTICAST method.
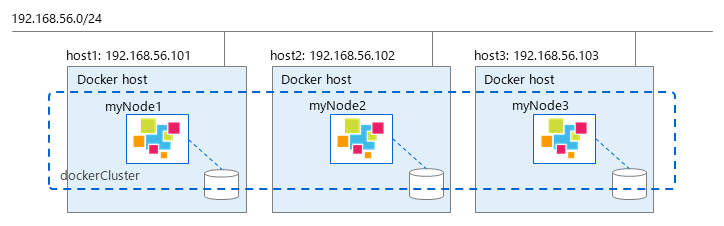
On host1:
$ docker run --net=host \
-e GRIDDB_NODE_NUM=3 \
-e GRIDDB_CLUSTERNAME=dockerCluster \
-e NOTIFICATION_ADDRESS=239.0.0.2 \
-e SERVICE_ADDRESS=192.168.56.101 \
--name myNode1 griddb/griddb-server:5.0
On host2:
$ docker run --net=host \
-e GRIDDB_NODE_NUM=3 \
-e GRIDDB_CLUSTERNAME=dockerCluster \
-e NOTIFICATION_ADDRESS=239.0.0.2 \
-e SERVICE_ADDRESS=192.168.56.102 \
--name myNode2 griddb/griddb-server:5.0
On host3:
$ docker run --net=host \
-e GRIDDB_NODE_NUM=3 \
-e GRIDDB_CLUSTERNAME=dockerCluster \
-e NOTIFICATION_ADDRESS=239.0.0.2 \
-e SERVICE_ADDRESS=192.168.56.103 \
--name myNode3 griddb/griddb-server:5.0
FIXED_LIST method
In FIXED_LIST method, you can use either macvlan or overlay network for containers. With macvlan network, each container uses the same subnet with docker host, so it is no need to expose ports. With overlay network, it is necessary to expose 3 ports: 10001, 20001 (when using NewSQL) and 10040.
The following commands will build a three-node GridDB cluster on 3 docker hosts in FIXED_LIST method using overlay network.
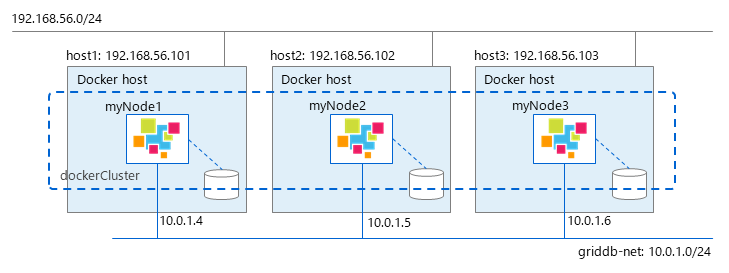
-
Using docker in swarm mode to create an overlay network
On host1:
$ docker swarm init --advertise-addr=192.168.56.101This command will return the token for other nodes to join the swarm
On host2:
$ docker swarm join --token <TOKEN> \ --advertise-addr 192.168.56.102 192.168.56.101:2377On host3:
$ docker swarm join --token <TOKEN> \ --advertise-addr 192.168.56.103 192.168.56.101:2377 - Create an overlay network (griddb-net)
$ docker network create -d overlay \ --subnet 10.0.1.0/24 --attachable griddb-net -
Start GridDB server containers:
On host1:
$ docker run \ -e GRIDDB_NODE_NUM=3 \ -e GRIDDB_CLUSTERNAME=dockerCluster \ -e NOTIFICATION_MEMBER=10.0.1.4,10.0.1.5,10.0.1.6 \ -p 10001:10001 -p 10040:10040 -p 20001:20001 \ --network griddb-net --ip 10.0.1.4 \ --name myNode1 griddb/griddb-server:5.0On host2:
$ docker run -e GRIDDB_NODE_NUM=3 \ -e GRIDDB_NODE_NUM=3 \ -e GRIDDB_CLUSTERNAME=dockerCluster \ -e NOTIFICATION_MEMBER=10.0.1.4,10.0.1.5,10.0.1.6 \ -p 10001:10001 -p 10040:10040 -p 20001:20001 \ --network griddb-net --ip 10.0.1.5 \ --name myNode2 griddb/griddb-server:5.0On host3:
$ docker run -e GRIDDB_NODE_NUM=3 \ -e GRIDDB_NODE_NUM=3 \ -e GRIDDB_CLUSTERNAME=dockerCluster \ -e NOTIFICATION_MEMBER=10.0.1.4,10.0.1.5,10.0.1.6 \ -p 10001:10001 -p 10040:10040 -p 20001:20001 \ --network griddb-net --ip 10.0.1.6 \ --name myNode3 griddb/griddb-server:5.0 -
Modify 2 files:
gs_node.jsonandgs_cluster.jsonin each container:gs_node.jsonof myNode1: Modify/transaction/serviceAddressand/sql/serviceAddressto “192.168.56.101”gs_node.jsonof myNode2: Modify/transaction/serviceAddressand/sql/serviceAddressto “192.168.56.102”gs_node.jsonof myNode3: Modify/transaction/serviceAddressand/sql/serviceAddressto “192.168.56.103”gs_cluster.jsonof 3 nodes:{ ... "cluster": { ... "notificationMember": [ { "cluster": {"address": "10.0.1.4","port": 10010}, "sync": {"address": "10.0.1.4","port": 10020}, "system": {"address": "10.0.1.4","port": 10040}, "transaction": {"address": "192.168.56.101","port": 10001}, "sql": {"address": "192.168.56.101","port": 20001} }, { "cluster": {"address": "10.0.1.5","port": 10010}, "sync": {"address": "10.0.1.5","port": 10020}, "system": {"address": "10.0.1.5","port": 10040}, "transaction": {"address": "192.168.56.102","port": 10001}, "sql": {"address": "192.168.56.102","port": 20001} }, { "cluster": {"address": "10.0.1.6","port": 10010}, "sync": {"address": "10.0.1.6","port": 10020}, "system": {"address": "10.0.1.6","port": 10040}, "transaction": {"address": "192.168.56.103","port": 10001}, "sql": {"address": "192.168.56.103","port": 20001} } ] ... } ... }
PROVIDER method
PROVIDER method is the same as FIXED_LIST method On docker host with overlay network, 3 ports: 10001, 20001 (when using NewSQL) and 10040 must be exposed.
The following commands will build a three-node GridDB cluster on 3 docker hosts in PROVIDER method using overlay network.
Assume that the provider host is http://192.168.56.104/provider.json and provides the following host information:
$ curl http://192.168.56.104/provider.json
[
{
"cluster": {"address": "10.0.1.4","port": 10010},
"sync": {"address": "10.0.1.4","port": 10020},
"system": {"address": "10.0.1.4","port": 10040},
"transaction": {"address": "192.168.56.101","port": 10001},
"sql": {"address": "192.168.56.101","port": 20001}
},
{
"cluster": {"address": "10.0.1.5","port": 10010},
"sync": {"address": "10.0.1.5","port": 10020},
"system": {"address": "10.0.1.5","port": 10040},
"transaction": {"address": "192.168.56.102","port": 10001},
"sql": {"address": "192.168.56.102","port": 20001}
},
{
"cluster": {"address": "10.0.1.6","port": 10010},
"sync": {"address": "10.0.1.6","port": 10020},
"system": {"address": "10.0.1.6","port": 10040},
"transaction": {"address": "192.168.56.103","port": 10001},
"sql": {"address": "192.168.56.103","port": 20001}
}
]
-
Using docker in swarm mode to create an overlay network
On host1:
$ docker swarm init --advertise-addr=192.168.56.101This command will return the token for other nodes to join the swarm.
On host2:
$ docker swarm join --token <TOKEN> \ --advertise-addr 192.168.56.102 192.168.56.101:2377On host3:
$ docker swarm join --token <TOKEN> \ --advertise-addr 192.168.56.103 192.168.56.101:2377 - Create an overlay network (griddb-net)
$ docker network create -d overlay \ --subnet 10.0.1.0/24 --attachable griddb-net -
Start GridDB server containers:
On host1:
$ docker run -e GRIDDB_NODE_NUM=3 \ -e GRIDDB_CLUSTERNAME=dockerCluster \ -e NOTIFICATION_PROVIDER=http://192.168.56.104/provider.json \ -p 10001:10001 -p 10040:10040 -p 20001:20001 \ --network griddb-net --ip 10.0.1.4 \ --name myNode1 griddb/griddb-server:5.0On host2:
$ docker run -e GRIDDB_NODE_NUM=3 \ -e GRIDDB_CLUSTERNAME=dockerCluster \ -e NOTIFICATION_PROVIDER=http://192.168.56.104/provider.json \ -p 10001:10001 -p 10040:10040 -p 20001:20001 \ --network griddb-net --ip 10.0.1.5 \ --name myNode2 griddb/griddb-server:5.0On host3:
$ docker run -e GRIDDB_NODE_NUM=3 \ -e GRIDDB_CLUSTERNAME=dockerCluster \ -e NOTIFICATION_PROVIDER=http://192.168.56.104/provider.json \ -p 10001:10001 -p 10040:10040 -p 20001:20001 \ --network griddb-net --ip 10.0.1.6 \ --name myNode3 griddb/griddb-server:5.0 -
Modify file
gs_node.jsonin each container, (gs_cluster.jsonis not necessaty)gs_node.jsonof myNode1: Modify/transaction/serviceAddressand/sql/serviceAddressto “192.168.56.101”gs_node.jsonof myNode2: Modify/transaction/serviceAddressand/sql/serviceAddressto “192.168.56.102”gs_node.jsonof myNode3: Modify/transaction/serviceAddressand/sql/serviceAddressto “192.168.56.103”
— Operations —
Start a shell in a container
$ docker exec -it <node_name> bash
Check GridDB cluster status
$ docker exec -it <node_name> bash
$ su - gsadm
$ gs_stat -u admin/admin
Access to GridDB cluster
Access GridDB cluster in MULTICAST mode from docker host
- Set a multicast route from the host network to the container’s docker0 interface.
$ ip route add 239.0.0.1/32 dev docker0 - The client accesses the multicast route
$ cd sample $ javac -cp /usr/share/java/gridstore.jar MultiNodesClient.java $ java -cp .:/usr/share/java/gridstore.jar MultiNodesClient 239.0.0.1 31999 myCluster
Access from GridDB client outside Docker host
- Keep the necessary ports exposed when starting the container
$ docker run -P -d --name griddb griddb/griddb-server:5.0or forward port:
$ docker run -p 40001:10001 -d --name griddb griddb/griddb-server:5.0 - You can check the exposed port with the following command
$ docker port griddb - The client accesses the exposed port
$ cd sample $ javac -cp /usr/share/java/gridstore.jar SingleNodeClient.java $ java -cp .:/usr/share/java/gridstore.jar SingleNodeClient <Docker Host IP Address> 40001 myCluster
— Trademark —
- GridDB is a registered trademark of Toshiba Digital Solutions Corporation in Japan.
- Docker is a registered trademark of Docker Inc. in the United States and other countries.